Music has always been a large part of my life, as for many others. It has the power to take us back in time and capture a moment.
Over a year ago, I became hyper-sensitive to the type of music I was listening to. Maybe it was a God thing, I truly don’t know, but I noticed that a certain type of music elevated my ego.
At this same time, I was trying to rid myself of an obsession with fitness and vanity. Sounds deep, I know, but it was.
I began to connect the dots on the things that kept me tethered to the lifestyle, and one of them was music. Until this point in my life, I didn’t realize the impact music can have.
So I changed what I was listening to, and guess what happened? I changed too! Side note this was not the only thing I changed but it was a major component.
Like many abstract things in life such as music there is a science that can explain the inner workings.
However, the science did not prompt me to change what I was listening to. The inner prompt we get and many times ignore did.
Science only confirmed that music can, in fact, change our behavior. It is also a tool that can change our perception; others may also know this and use it to their advantage. I am not a conspiracist, but I sure know there are no coincidences.
So going down the rabbit hole as I love to do, here is what I found…
~

Photo by Hal Gatewood on Unsplash
What are brain waves?
Our brain is the organ that controls approximately 600 muscles in our body. The three main types of muscle include skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. The brain, nerves, and skeletal muscles work together to cause movement, collectively known as the neuromuscular system.
The muscles in our body are made of tissue grouped into elastic bundles that contract to produce motion.
Our brain is the command center that controls thought, memory, emotion, touch, motor skills, vision, breathing, temperature, hunger, and every process that regulates our body. The brain and spinal cord that extends from it work together, controlling our body movements and functions; this is the makeup of our central nervous system.
Brain waves are at the root of our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors; synchronized electrical pulses produce them. These pulses are from our neurons that communicate with each other as information messengers.
They use electrical impulses and chemical signals to transmit information between different areas of the brain and between the brain and the rest of the nervous system; the activity is divided into bandwidths (chart below).
Brainwaves can be viewed as music notes – the low-frequency waves are like a deeply penetrating drum beat, while the higher-frequency brainwaves are more like high-pitched flutes.
Our brainwaves change according to what we’re doing and feeling. We can feel tired, slow, and sluggish when slower brainwaves are dominant, and when the higher frequencies are dominant, we feel hyper-alert.
~
Brainwave speed is measured in Hertz (cycles per second), and they are divided into bands best described as slow, moderate, and fast waves.
| Frequency band | Frequency | Brain states |
| Gamma (γ) | 38-42 Hz | Heightened Awareness |
| Beta (β) | 12–35 Hz | Problem-Solving |
| Alpha (α) | 8–12 Hz | Relaxed Reflection |
| Theta (θ) | 4–8 Hz | Mediation & Creativity |
| Delta (δ) | 0.5–4 Hz | Deep sleep |
How do our brainwaves affect us daily?
Research has identified brainwave patterns; our daily experiences in the world and our brainwaves are inseparable. When our brainwaves are out of balance, there will be related problems in our emotional or neuro-physical health. Emotional and neurological conditions directly correspond to our brainwaves.
Brainwaves stimulate our voluntary movements and thoughts. A simulant can produce over-arousal and under-arousal in specific areas of the brain; a state of arousal could alter one of the brain’s decision-making centers. Various stimulants can alter brain chemistry, such as food, caffeine medications, and recreational drugs. Music can also alter brainwaves and their activity, being an emotionally charged sensory stimulant.
Over-arousal in specific brain areas is linked with the following:
- anxiety disorders
- sleep problems
- nightmares
- hyper-vigilance
- impulsive behavior
- anger/aggression
- agitated depression
- chronic nerve pain
- spasticity
Under-arousal in certain parts of the brain can lead to:
- depression
- attention deficit
- chronic pain
- insomnia.
A lack of stability in brain rhythms is directly linked with the following:
- tics
- obsessive-compulsive disorder
- aggressive behavior, rage, explosive behavior.
- grind, gnash, or clench teeth
- panic attacks
- bipolar disorder
- migraines
- narcolepsy, sleep apnea
- epilepsy,
- vertigo – the sensation that you, or the environment around you, is moving or spinning.
- “hearing” noises in your ears
- anorexia/bulimia
- diabetes, hypoglycemia
~
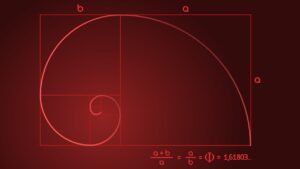
Image by Rafael Javier from Pixabay
How does altering our brainwaves affect us?
Any process that changes your perception changes your brainwaves. As stated previously, chemicals and sounds can alter our brainwaves.
432 hertz is the frequency closest to that of the sound of nature, which the universe vibrates; some call it the “heartbeat of the Earth.”
According to an article written by Schiller Institute, the most scientifically correct tuning is 432 Hz. The mathematical calculations by which this conclusion was arrived at are known as Fibonacci Sequence.
~
432 Herts VS 440 Herts
The mathematical equation produced can be calculated starting from the octave of the A4 = 432 Hz, in which the C4 (DO3) corresponds to 256 Hz. The following is the mathematical relation: 256/2 = 128 Hz (C3); 128/2 = 64 Hz (C2); 64/2 = 32 Hz (C1); 32/2 = 16 Hz (C0); 16/2 = 8 Hz (C-1). The terrestrial frequency is about 8 Hz, Schumann resonance.
This same mathematical relationship does not exist at 440 Hz because the C4 (DO3) corresponds to 261.63 Hz. Because of this harmonic misalignment, listening to 440 Hz music makes people anxious, nervous, or aggressive because it is not in harmony with the natural frequency of the planet earth.
This should tell us something about music tuned at 440 Hz.
432 Hz is especially pleasing to the ear, reduces stress, and promotes emotional stability, aiding a calmer, happier, and relaxed state of mind.
~
The Benefits of Music Tuned at 432Hz
“Our DNA is sensitive to frequencies. Human DNA is sensitive to music and its relative frequencies to the point that it can even be reprogrammed through them. In fact, by subjecting stem cells to various frequencies, it has been possible to modify their natural organic function.” -The Professor Carlo Ventura’s team.
Photo by Marius Masalar on Unsplash
